Sliding Window
This pattern focuses on traversing arrays (or linked lists). The idea is that we are looking for some (contiguous) sub-array with a particular property. We keep track of some indices that define our "window" (a sub-array) and iteratively "slide" the window in order to perform a search of sub-arrays. Sliding can mean shrinking or growing the window in any direction, or moving the window left or right any amount without changing the size.
A few things to remember about sliding the window
-
We want to slide the window based on either simple local criteria or the same way every time
- example of same way every time: just move the window left by one each time (without changing the window size)
- example of based on simple criteria: grow the window leftward by one if the sum of the subarray is negative, or shrink the window leftward
-
We often need to keep track of some property of the subarray (for example the sum, the average, the number of negative elements). To get the best runtime we should figure out how to update this property without recomputing it from the whole subarray. Instead, update the property using the elements that are being added or removed from the window.
Now consider the following problem:
Average of each size K-subarray
Given an array of integers, return in a new array the average of each subarray of length . (Do this in order starting with the subarray that is the furthest left)
Example instance where the answer is [5, 7, 5, 8, 13]:
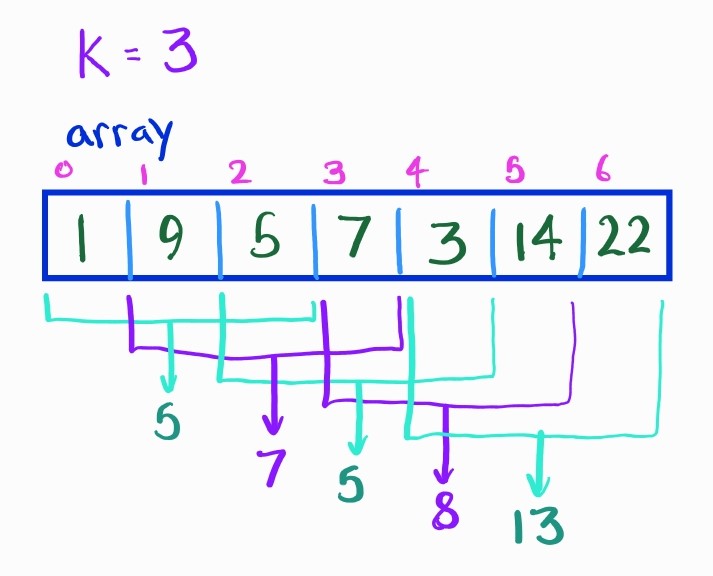
The naïve solution to this problem is to iterate through each subarray one at a time like so:
- slide the window rightward by one each time (not changing the size) until we reach the end
- add up all the elements of the subarray, and divide this number by
- append this new average to the list we will return at the end
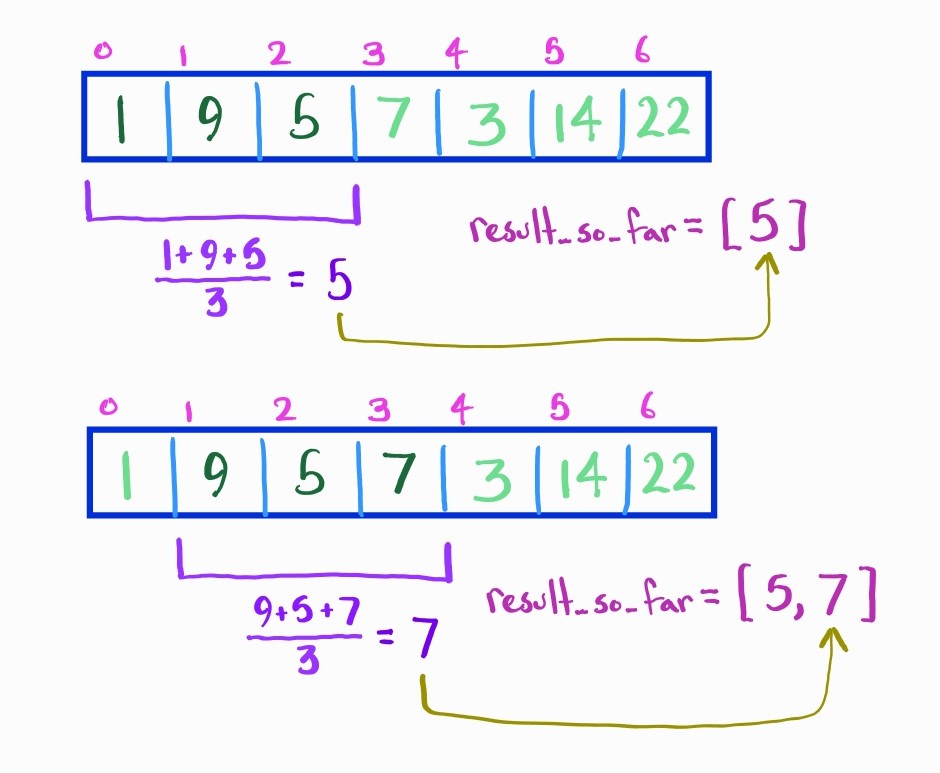
This solution yields a run-time of where is the length of our input array. This comes from searching through sub-arrays and doing work to compute each subarray average.
We can improve our runtime by not recalculating our average from scratch. Instead, keep track of the current sum of the subarray. Update the sum after sliding the window by adding the element on the right that moves into the window and subtracting the element on the left that moves out of the window. Each time, add this sum divided by to the list of subarray averages to be returned.
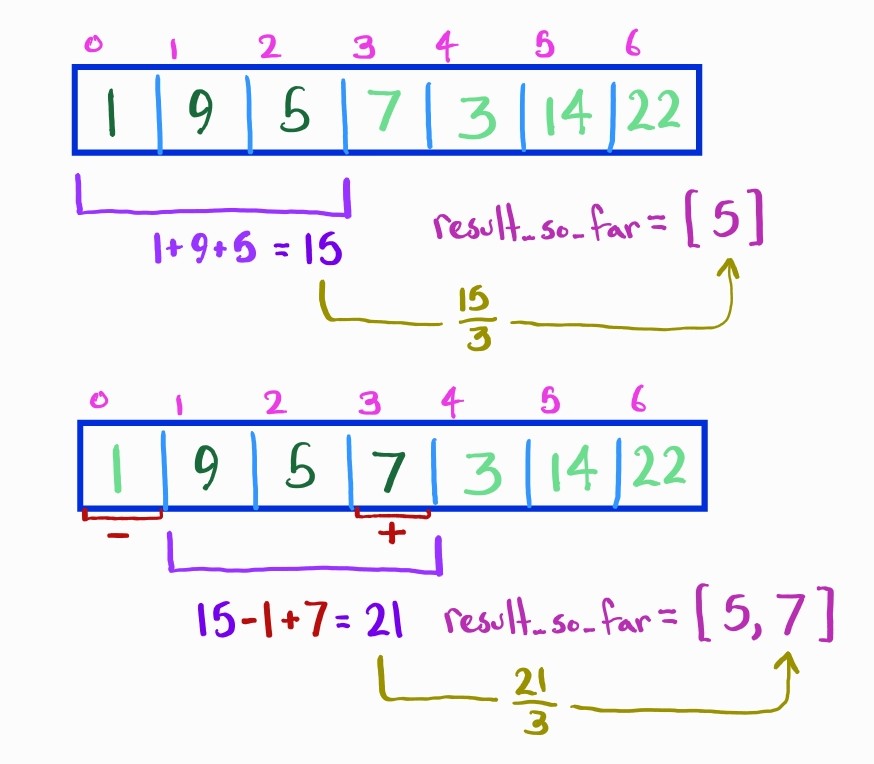
This solution yields a run-time of where is the length of our input array. We still search through sub-arrays, but now we do work to compute each subarray average.
Problems for this Week
(easy) maximum-average-subarray-i
You are given an integer array
numsconsisting ofnelements, and an integerk. Find a contiguous subarray whose length is equal tokthat has the maximum average value and return this value. Any answer with a calculation error less than10-5will be accepted.
(easy) minimum-difference-between-highest-and-lowest-of-k-scores
You are given a 0-indexed integer array
nums, wherenums[i]represents the score of theithstudent. You are also given an integerk. Pick the scores of anykstudents from the array so that the difference between the highest and the lowest of thekscores is minimized. Return the minimum possible difference.
(easy) find-the-k-beauty-of-a-number
The k-beauty of an integer
numis defined as the number of substrings ofnumwhen it is read as a string that meet the following conditions:
- It has a length of
k.- It is a divisor of
num.Given integers num and k, return the k-beauty of num.
Note: Leading zeros are allowed, 0 is not a divisor of any value.
(A substring is a contiguous sequence of characters in a string)
Tip: I recommend turning the
intinto astringwith built-in methods to begin (e.g.str(my_int)in python), this makes it easier to get the subsets of decimal digits. Modulo arithmetic is not the focus of this question. Then after turn the string into an int again to check if it is divisible by a number.
(easy) minimum-recolors-to-get-k-consecutive-black-blocks
You are given a 0-indexed string
blocksof lengthn, whereblocks[i]is either'W'or'B', representing the color of theithblock. The characters'W'and'B'denote the colors white and black, respectively. You are also given an integerk, which is the desired number of consecutive black blocks. In one operation, you can recolor a white block such that it becomes a black block. Return the minimum number of operations needed such that there is at least one occurrence ofkconsecutive black blocks.
(medium) maximum-subarray
Given an integer array
nums, find the subarray with the largest sum, and return its sum
(medium) minimum-size-subarray-sum
Given an array of positive integers
numsand a positive integertarget, return the minimal length of a subarray whose sum is greater than or equal to target. If there is no such subarray, return 0 instead.
(medium) fruit-into-baskets
You are visiting a farm that has a single row of fruit trees arranged from left to right. The trees are represented by an integer array
fruitswherefruits[i]is the type of fruit theithtree produces. You want to collect as much fruit as possible. However, the owner has some strict rules that you must follow:
- You only have two baskets, and each basket can only hold a single type of fruit. There is no limit on the amount of fruit each basket can hold.
- Starting from any tree of your choice, you must pick exactly one fruit from every tree (including the start tree) while moving to the right. The picked fruits must fit in one of your baskets.
- Once you reach a tree with fruit that cannot fit in your baskets, you must stop.
Given the integer array
fruits, return the maximum number of fruits you can pick.
(medium) longest-substring-without-repeating-characters
Given a string s, find the length of the longest substring without repeating characters.
(medium) longest-repeating-character-replacement
You are given a string
sand an integerk. You can choose any character of the string and change it to any other uppercase English character. You can perform this operation at mostktimes. Return the length of the longest substring containing the same letter you can get after performing the above operations.
(medium) max-consecutive-ones-iii
Given a binary array
numsand an integerk, return the maximum number of consecutive1's in the array if you can flip at mostkzeros.
(medium) permutation-in-string
Given two strings
s1ands2, returntrueifs2contains a permutation ofs1, orfalseotherwise. In other words, returntrueif one ofs1's permutations is the substring ofs2.
(medium) find-all-anagrams-in-a-string
Given two strings
sandp, return an array of all the start indices ofp's anagrams ins. You may return the answer in any order. An Anagram is a word or phrase formed by rearranging the letters of a different word or phrase, typically using all the original letters exactly once.
(medium) minimum-window-substring
Given two strings
sandtof lengthsmandnrespectively, return the minimum window substring ofssuch that every character int(including duplicates) is included in the window. If there is no such substring, return the empty string"". The testcases will be generated such that the answer is unique.
(medium) substring-with-concatenation-of-all-words
You are given a string
sand an array of stringswords. All the strings ofwordsare of the same length. A concatenated substring insis a substring that contains all the strings of any permutation ofwordsconcatenated.
- For example, if
words = ["ab","cd","ef"], then"abcdef","abefcd","cdabef","cdefab","efabcd", and"efcdab"are all concatenated strings."acdbef"is not a concatenated substring because it is not the concatenation of any permutation ofwords.Return the starting indices of all the concatenated substrings in
s. You can return the answer in any order.